Table of contents
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) Market Poised for Growth
- Servers Application Segment is Expected to Hold Significant Market Share
- The APAC region is expected to drive market growth during the forecasted period
- GPU Market Customer Landscape
- Market Overview
- Current Trends and Insights
- Crypto AI projects would need to purchase chips worth their entire market capitalization to achieve their goals.
- How did Nvidia generate such high revenue in the fiscal year 2024?
- GPU sales saw 32% year-over-year increase in Q4 — AMD's market share rises to 19%
- Need Army of 720,000 Nvidia H100 GPUs
- Nvidia isn't the only game in town
- How DePIN Democratizes Innovation, Overcome GPU Shortages and Establish Trust
An electronic circuit/chip, a graphics processing unit (GPU), is designed to manipulate and alter memory to accelerate image creation in a frame buffer intended for display output. GPUs are utilized in various platforms, such as game consoles, personal computers, workstations, mobile devices, electronic equipment, and embedded systems.
As per the Indian Electrical Equipment Industry Mission Plan 2012-2022, the Indian government aims to transform the country into an electrical equipment manufacturer and achieve a productivity of USD 100 billion by matching exports and imports.
With the widespread use of computing devices, such as laptops and personal computers (PCs), and a surge in investment in the electronics and automobile sector, the GPU market has witnessed significant growth in recent years. Additionally, the expansion of technologies like AI, the trend of real-time analysis, and the increasing demand for high-end graphics and computing applications are expected to drive further growth in the graphics processing unit market over the forecast period.
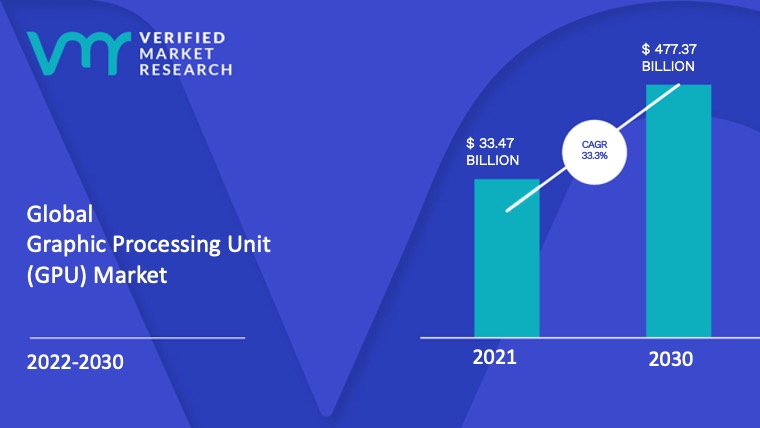
Graphic Processing Unit (GPU) Market size was valued at USD 33.47 Billion in 2021 and is projected to reach USD 477.37 Billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 33.3% from 2022 to 2030.
Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) Market Poised for Growth
The Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) Market is projected to achieve a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 33.3% during the forecast period. The market was valued at USD 37.9 billion last year and is anticipated to reach USD 206.95 billion within the next five years.
In recent years, there has been a surge in demand for high-end personal computing devices and gaming consoles, driving the need for graphics add-in boards, which are crucial components of the final product. The market's growth has been fueled by the widespread adoption of computing devices such as personal computers (PCs) and laptops globally, alongside increased investments in the gaming industry.
The expansion of technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the trend towards real-time analysis are broadening the scope of GPU technology over the forecast period, driven by the demand for high graphics and computing applications. The gaming industry stands out as a significant driver for the GPU market, with increasing investments and advancements in game development leading to a higher demand for high-graphics capabilities.
Emerging technologies such as Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), and AI are driving further demand for GPUs due to their requirement for high-speed analysis, making GPUs an ideal choice. Despite AI chips surpassing GPUs in performance and energy efficiency, GPUs remain integral to high-performance computing due to their solid general-purpose computing capability.
Manufacturing standalone GPU chips entails high costs and necessitates high-end machinery despite the cost-effectiveness of raw materials, leading companies to make significant initial investments in testing and manufacturing facilities.
The COVID-19 pandemic initially disrupted the GPU industry's supply chain but subsequently led to increased consumer demand in specific segments, supporting the growth of GPU technology. In April of this year, Nvidia utilized high-performance computing with NVIDIA GPUs to analyze data from the Hubble telescope, enhancing understanding of various planets.
Servers Application Segment is Expected to Hold Significant Market Share
The server application segment is projected to capture a substantial share of the GPU market due to the increasing adoption of cloud services across different industries. As an example, KDDI, a major Japanese telecommunications company, collaborated with NVIDIA to provide its GeForce Now game-streaming service to customers through a low-latency broadband and 5G network, utilizing NVIDIA's RTX gaming servers installed in a new data center in Tokyo.
GPU-as-a-Service (GPUaaS) has gained popularity for several applications, such as training multilingual AI speech engines and detecting early signs of diabetic retinopathy. Modern GPUaaS offers faster processing at lower costs without requiring capital expenditures than conventional general-purpose processors.
In addition, there is growing interest in the Indian market from GPU vendors, with Acer launching new NVIDIA Tesla GPU-powered servers in India. These servers feature up to eight NVIDIA Tesla V100 32GB SXM2 GPU accelerators and PCIe slots for high-speed connectivity.
Advancements in high-performance computing (HPC) technology have opened up opportunities for GPU manufacturers. For instance, scientists recently employed a supercomputer equipped with NVIDIA GPUs to identify patterns in Hubble data related to 25 exoplanets, enhancing our comprehension of their fiery atmospheres. Furthermore, according to Steam, approximately 91.22% of users utilize DirectX 12 GPU graphics cards as of August 2022.
The APAC region is expected to drive market growth during the forecasted period
The graphics processing unit market is expected to dominate the Asia Pacific region during the forecast period. The region is witnessing a surge in demand for electronic devices such as smartphones and laptops, particularly in countries such as China and India, thereby driving the regional economy. According to the International Data Corporation, India delivered 14.8 million units of personal computers (PCs) in calendar 2021, reflecting a 44.5% YoY increase. The country's PC industry witnessed successful shipment growth, including desktops, notebooks, and workstations.
Furthermore, the increasing expenditure on data centers and research centers across the Asia Pacific region is projected to boost the demand for graphics processing units. The Ministry of Finance announced in February 2023 that three centers of excellence for artificial intelligence (AI) will be established under the National Data Governance Policy, providing access to anonymized data in these data centers.
The demand for graphics processing units in the Asia Pacific region will increase dramatically, as evidenced by the government's announcement to construct one of two data center clusters in the Yangtze River Delta Ecological Green Integrated Development Demonstration Zone in Shanghai, Suzhou (Jiangsu Province), and Jiaxing (Zhejiang Province). As more countries in the Asia Pacific region invest in data centers and the demand for electronic devices continues to soar, the graphics processing unit market is expected to experience robust growth.
For more insights on the market share of various regions, Download PDF Sample now!
According to estimates, APAC is set to contribute 42% to the global market growth and forecasting during the forecast period. The US and France are the only two countries that have come close to contributing to market growth. Technavio’s analysts have meticulously elaborated on the regional trends and drivers shaping the market during the forecast period. APAC is a clear leader in the global market, thanks to various factors such as technological advancements, growing demand for gaming and virtual reality applications, and significant regional market players.

What sets APAC apart is the presence of major players such as NVIDIA, AMD, and Intel, who play a crucial role in influencing the industry. These companies deliver cutting-edge solutions to cater to the growing demand of various regional industries. Furthermore, the region boasts a well-developed electronics manufacturing industry that allows companies to produce at competitive prices. As a result, manufacturers are flocking to establish their production facilities in APAC, further bolstering the market dominance of the region.
GPU Market Customer Landscape
The market report includes the adoption lifecycle of the market, covering from the innovator’s stage to the laggard’s stage. It focuses on adoption rates in different regions based on penetration. Furthermore, the report includes key purchase criteria and drivers of price sensitivity to help companies evaluate and develop their growth strategies.
Market Overview
To learn more about this report, View the Report Sample
Current Trends and Insights
The adoption of AI and ML is an undeniable trend shaping market growth. The market is currently experiencing a major shift towards implementing these technologies. This increase can be attributed solely to the numerous benefits that AI and ML bring, making them highly sought-after technologies. Their ability to significantly enhance the overall processing performance is one of the primary reasons behind the growing adoption of AI and ML in the market.
AI and ML algorithms can process large amounts of data at lightning-fast speeds, allowing for real-time visual computing and rendering. This is especially critical in the gaming, VR, and AR industries, where high-quality graphics and smooth performance are paramount.
Furthermore, the growing adoption of AI and ML is also driven by the remarkable advancements in hardware and software. With powerful tools and libraries to harness the capabilities of AI and ML tasks, software frameworks such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, and CUDA provide developers with many options to explore. Therefore, these factors are expected to significantly increase the demand for AI and ML in the market, which will undoubtedly show positive results during the forecast period.
Crypto AI projects would need to purchase chips worth their entire market capitalization to achieve their goals.
Hundreds of graphics processing units (GPUs) will be required for mainstream text-to-video generation. This number is currently more than what Microsoft, Meta, and Google combined possess. The first demo of OpenAI's text-to-video generator Sora amazed the world, leading to a surge in interest in Artificial Intelligence (AI) tokens. As a result, several crypto AI projects emerged, promising to deliver text-to-video and text-to-image generation. According to CoinGecko data, the AI token category has a $25 billion market cap. Behind the promise of AI-generated videos are armies of Graphics Processing Units (GPUs), the processors from the likes of Nvidia and AMD, which make the AI revolution possible thanks to their ability to compute large volumes of data. But how many GPUs will it take to make AI-generated video mainstream? The answer is more than what major big tech companies had in their arsenal in 2023.
ChatGPT, hailed by Bill Gates as “as revolutionary as mobile phones and the internet”, has become hugely popular worldwide. This intelligent chatbot heavily relies on high-performance GPU chips to train models, as its underlying technology is AI natural language processing. Therefore, the recent popularity of ChatGPT has led to a surge in market demand and market heat for products from NVIDIA of which have GPU computing power as their core. Specifically, after NVIDIA’s stock price dropped nearly 60% in the first half of 2022, its market value rose 85% in the past three months of 2023, thanks to ChatGPT.
According to data, NVIDIA's market cap was $2.265 trillion as of April 2024, making it the world's third-most valuable company by market cap.

How did Nvidia generate such high revenue in the fiscal year 2024?
Nvidia's success in the past year was inevitable, given the company's years of hard work in building a comprehensive and integrated stack of chips, systems, software and services for accelerated computing, with a primary focus on data centers, cloud computing and edge computing. The company found itself at the center of a massive demand cycle due to the hype around generative AI, which was mainly kicked off by the late 2022 arrival of OpenAI's ChatGPT, a chatbot powered by a large language model that can understand complex prompts and respond with an array of detailed answers.
The tech industry found more promise than concern with the capabilities of ChatGPT and other generative AI applications that had emerged in 2022, like the DALL-E 2 and Stable Diffusion text-to-image models. Many of these models and applications had been trained and developed using Nvidia GPUs because the chips are far faster at computing such large amounts of data than CPUs ever could.
The enormous potential of these generative AI applications kicked off a massive wave of new investments in AI capabilities by companies of all sizes, from venture-backed startups to cloud service providers and consumer tech companies, like Amazon Web Services and Meta.
Nvidia's data center GPU, the H100, with a new feature called the Transformer Engine, was designed to speed up the training of transformer models by as many as six times compared to the previous-generation A100. Among the transformer models that benefitted from the H100's Transformer Engine was GPT-3.5, short for Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3.5. This is OpenAI's large language model that exclusively powered ChatGPT before the introduction of the more capable GPT-4.
Nvidia's CUDA parallel computing platform and programming model allowed the company's GPUs to run HPC workloads faster than CPUs by breaking them down into smaller tasks and processing those tasks simultaneously. Since its introduction in 2007, CUDA has dominated the landscape of software that benefits accelerated computing.
Over the last several years, Nvidia's stack has grown to include CPUs, SmartNICs and data processing units, high-speed networking components, pre-integrated servers and server clusters as well as a variety of software and services, which includes everything from software development kits and open-source libraries to orchestration platforms and pretrained models.
Nvidia's data center business grew by 217% to $47.5 billion in its 2024 fiscal year, which represented 78% of total revenue. This was mainly supported by a 244% increase in data center compute sales, with high GPU demand driven mainly by the development of generative AI and large language models. Cloud service providers and consumer internet companies contributed a substantial portion of Nvidia's data center revenue, with the former group representing roughly half and then more than a half in the third and fourth quarters, respectively.
Nvidia's CEO Jensen Huang stated that this represents the industry's continuing transition from general-purpose computing, where CPUs were the primary engines, to accelerated computing, where GPUs and other kinds of powerful chips are needed to provide the right combination of performance and efficiency for demanding applications.
GPU sales saw 32% year-over-year increase in Q4 — AMD's market share rises to 19%
According to a report from Jon Peddie Research, the discrete graphics card market saw a remarkable recovery in Q4 of last year, with shipments rising by 6.8% compared to Q3 2023 and a staggering 32% compared to Q4 2022. Both Nvidia and AMD experienced growth in sales quarter-to-quarter and year-over-year, but AMD's growth was considerably higher, increasing its market share to 19%. The CPU market is also recovering, with shipments returning to 2022 levels.

Despite the COVID-19 pandemic driving up the sales of discrete GPUs in 2020 and 2021, shipments declined sharply in 2022, probably due to a globally weakening economy that led some countries into recession. However, the graphics card sales saw a significant recovery in 2023, and Q4 continued this trend with a 6.8% gain in shipments.
As a result of these consecutive quarterly increases in shipments, Q4 of 2023 witnessed 32% more discrete GPUs shipped than in Q4 of 2022. The difference is almost 40% compared to Q1 of 2023. Though Jon Peddie Research didn't elaborate much on the highlights of its GPU market report, rising desktop gaming GPU sales played a significant role in the increased sales seen in Q3, and perhaps that continued into Q4.
The CPU shipments are similarly recovering rapidly, with Q4 outperforming three of 2022's quarters. Though the CPU market has recovered better than the discrete graphics card market, it's still insufficient to put it on par with 2020 and 2021, which saw some of the highest shipments on record.
Intel's shipments were mostly flat among the three major GPU vendors, while Nvidia and AMD saw quarterly and yearly growth. Nvidia's shipments went up 4.7% from Q3 and 22.3% from Q4 of 2022, but that's nothing compared to AMD's gains of 17% quarter-to-quarter and 117% year-over-year. AMD has fueled a decent chunk of the GPU market's recovery in Q4 and 2023.
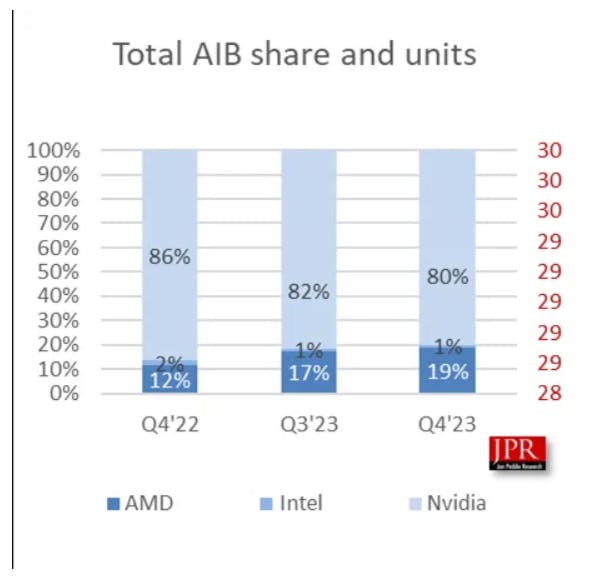
As AMD grew faster than Nvidia, its market share increased to 19% - up from 17% in Q3. AMD's market share is also up 7% compared to Q4 of 2022, which had been a terrible year for Radeon graphics cards. According to Jon Peddie Research, AMD was only at 10% market share in Q3 of 2022, likely the lowest since buying ATI and its Radeon graphics business in 2006. Although 17% is still relatively low, it's undoubtedly an improvement.
Jon Peddie, the founder of the eponymous research firm, states that GPU customers are "pretty damn happy and vote with their dollars," which explains the increasing shipments. Though the market seems to be "entering a golden age," Peddie warns us not to get ahead of ourselves and overreact, as we did in the past with crypto and Covid.
Need Army of 720,000 Nvidia H100 GPUs
According to the research report by Factorial Funds, it is estimated that a whopping 720,000 high-end Nvidia H100 GPUs will be required to support the creator community of TikTok and YouTube. In addition, Sora, as Factorial Funds has pointed out, requires up to 10,500 powerful GPUs for a month to train and can generate only about 5 minutes of video per hour per GPU for inference. As shown in the chart below, training this requires significantly more computing power than GPT4 or still image generation. However, with widespread adoption, inference will surpass training in compute usage. This implies that the computer power needed to create new videos (inference) will become greater than the power needed to train the AI model initially as more people and companies start using AI models like Sora to generate videos.
To put things in perspective, it is worth noting that Nvidia shipped 550,000 of the H100 GPUs in 2023. Data from Statista shows that the twelve largest customers using Nvidia's H100 GPUs collectively have 650,000 of the cards, and the two largest—Meta and Microsoft—have 300,000 between them. Assuming a cost of $30,000 per card, it would take $21.6 billion to bring Sora's dreams of AI-generated text-to-video mainstream, which is nearly the entire market cap of AI tokens.
It is important to note that even if you have the financial resources to acquire all the GPUs needed to support the TikTok and YouTube creator community, physically getting your hands on them could be challenging.
Nvidia isn't the only game in town
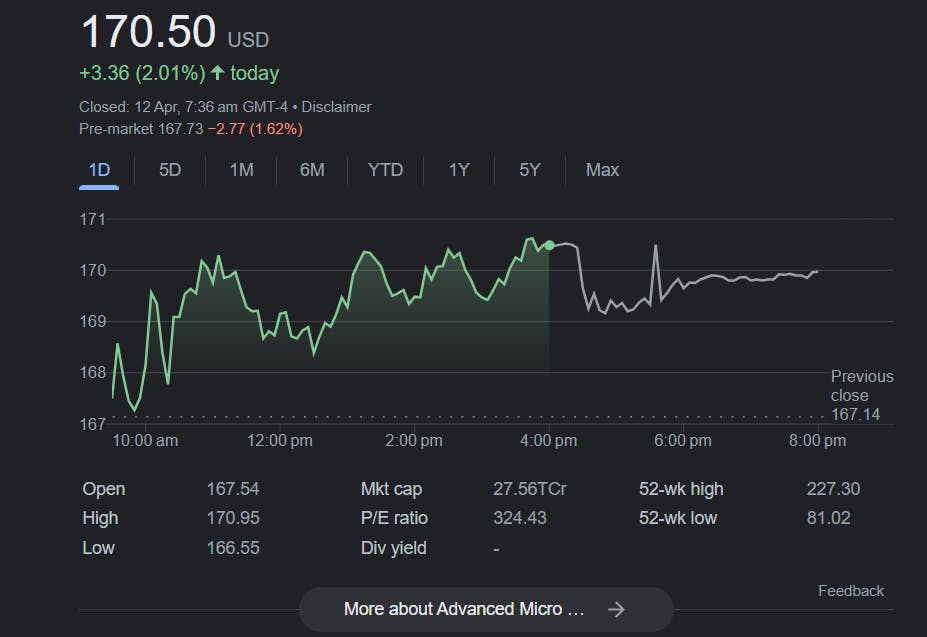
It's crucial to acknowledge that despite its reputation, Nvidia isn't the only player in the AI game. AMD, its long-time chip rival, offers competing products that investors have rewarded handsomely, driving its stock from the $2 range in 2012 to over $170 today.
While Render (RNDR) and Akash Network (AKT) offer distributed GPU computing, it's worth noting that most of the GPUs on these networks are retail-grade gaming GPUs, which are significantly less powerful than Nvidia's server-grade H100 or AMD's competition.
The text-to-video promise Sora and other protocols pledge will require a monumental hardware lift. Although it's an exciting premise that could revolutionize Hollywood's creative workflow, it's unlikely to become mainstream anytime soon. Simply put, we'll need more chips.
How DePIN Democratizes Innovation, Overcome GPU Shortages and Establish Trust
The GPU shortage will drive the mainstream adoption of Web3 infrastructure. High-end graphics processing units (GPUs) such as the NVIDIA A100s and H100s are essential for training artificial intelligence (AI) models. However, these GPUs are extremely expensive, have limited availability, and are only required for a short period for each model. This combination makes it impossible for many startups to own them.
Decentralized physical infrastructure networks (DePINs) provide the solution, particularly compute and storage networks. These networks will revolutionize AI and Web3 for two primary reasons: access and safety.
The emergence of AI will be the turning point for Web3 infrastructure since these protocols offer solutions to the data challenges and GPU shortages faced by AI startups. DePINs will transform AI development, making high-cost resources accessible to smaller players, democratizing AI innovation, and allowing hardware owners to generate passive income.
DePIN provides the antidote for trustworthy code and the physical infrastructure networks on which it runs. It's important to note that if startup founders build their apps on infrastructure controlled by internet Goliaths like Amazon Web Services (AWS), it becomes challenging for startups to compete since they have to pay a significant portion of their revenues to their competitors and take on counterparty risk.