The current revolution in generative AI owes its success to the large language models (LLMs). These AI systems, built on powerful neural architecture, are used to model and process human language and are the foundation of popular chatbots like ChatGPT and Google Bard. However, many of these models are proprietary and owned by Big Tech companies, which limits their accessibility and transparency. Thankfully, the open-source community has risen to the occasion by creating open-source LLMs that promise to make the field of generative AI more accessible, transparent, and innovative. In this article, we'll explore the top open-source LLMs available in 2024, which have already achieved significant milestones in just one year since the launch of ChatGPT and the popularization of (proprietary) LLMs.
The current revolution in generative AI owes its success to the large language models (LLMs). These AI systems, built on powerful neural architecture, are used to model and process human language and are the foundation of popular chatbots like ChatGPT and Google Bard. However, many of these models are proprietary and owned by Big Tech companies, which limits their accessibility and transparency. Thankfully, the open-source community has risen to the occasion by creating open-source LLMs that promise to make the field of generative AI more accessible, transparent, and innovative.
This article will explore the top open-source LLMs available in 2024. In just one year since the launch of ChatGPT and the popularization of (proprietary) LLMs, these LLMs have already achieved significant milestones.
Benefits of Using Open-Source LLMs
Choosing open-source LLMs has many benefits over proprietary LLMs, both short-term and long-term. Below is a list of the most compelling reasons:
Improved Data Security and Privacy: Open-source LLMs give companies complete control over personal data protection, eliminating the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access from third parties.
Cost Savings and Reduced Vendor Dependency: Unlike proprietary LLMs, open-source options do not require licensing fees, offering significant cost savings for businesses, particularly small and medium enterprises. However, keep in mind that running LLMs still demands substantial computational resources.
Code Transparency and Model Customization: Access to the source code, architecture, training data, and mechanisms of open-source LLMs enables better understanding, scrutiny, and tailored adjustments according to specific business needs.
Active Community Support and Innovation: Through global developer engagement, Open-source LLMs promote collaboration, innovation, and improved performance. They help address biases and enhance accuracy while encouraging eco-friendly advancements in AI.
Environmental Footprint Awareness: Unlike proprietary LLMs, open-source alternatives provide greater transparency regarding resource usage and environmental impact, paving the way for sustainable AI practices and innovations.
Top Open-Source Large Language Models For 2024
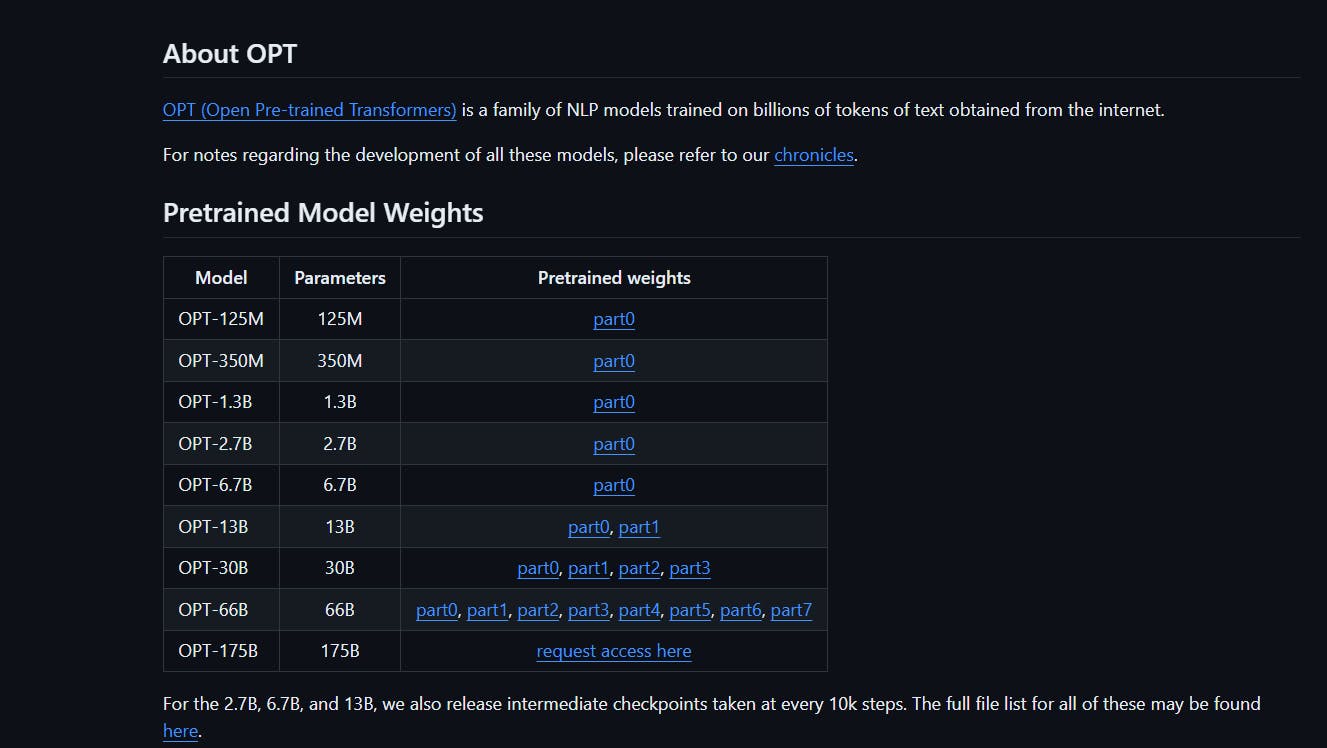
1. OPT-175B
The year 2022 saw the release of Open Pre-trained Transformers Language Models (OPT), a significant step towards Meta's mission to democratize the LLM industry through open-source technology.
OPT is a set of decoder-only pre-trained transformers ranging from 125M to 175B parameters. OPT-175B is one of the most advanced open-source LLMs available today, comparable in performance to GPT-3. Both the source code and pre-trained models are accessible to the public.
However, suppose you plan to develop an AI-driven company with LLMs. In that case, you should look for alternatives, as OPT-175B is released under a non-commercial license that only permits the use of the model for research purposes.
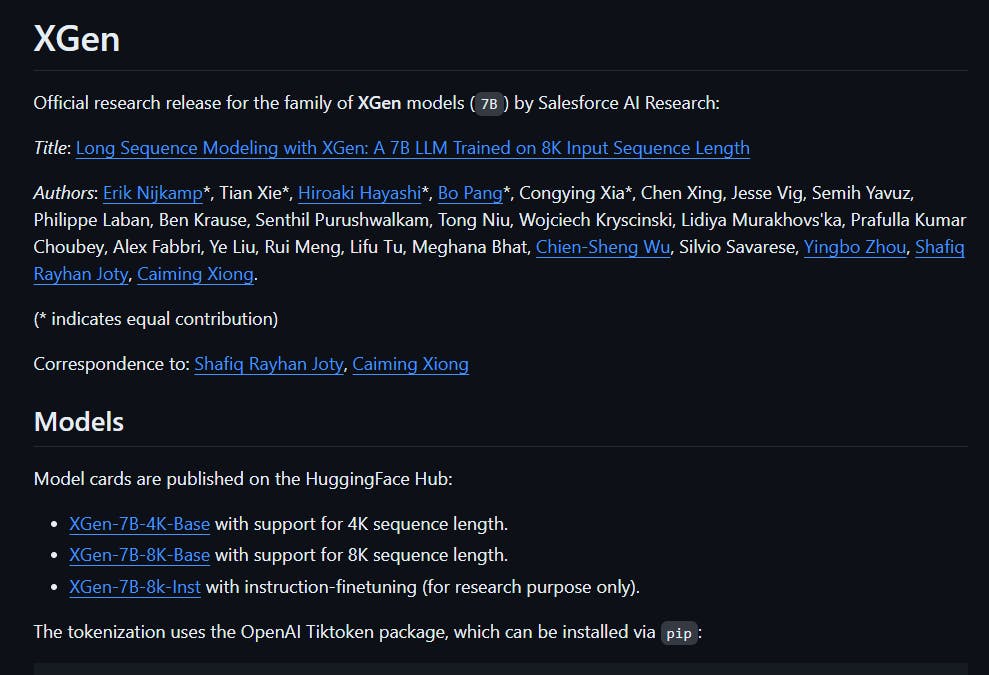
2. XGen-7B
Many companies are joining the LLM race, and Salesforce recently joined with its XGen-7B LLM in July 2023. Unlike most open-source LLMs, which provide limited information with short prompts, XGen-7B aims to provide a tool that supports longer context windows. The most advanced version of XGen (XGen-7B-8K-base) allows for an 8K context window, which includes the cumulative size of the input and output text.
Efficiency is also a top priority in XGen, which uses only 7B parameters for training, much less than other powerful open-source LLMs like LLaMA 2 or Falcon. Despite its smaller size, XGen can still deliver excellent results. The model is available for commercial and research purposes, except for the XGen-7B-{4K,8K}-inst variant, which is trained on instructional data and RLHF and is released under a noncommercial license.
3. GPT-NeoX and GPT-J
GPT-NeoX and GPT-J are two open-source alternatives to GPT, developed by researchers from EleutherAI, a non-profit AI research lab. Both are language models that can perform various natural language processing tasks, including text generation, sentiment analysis, research, and marketing campaign development.

GPT-NeoX has 20 billion parameters, while GPT-J has 6 billion parameters. Although most advanced language models can be trained with over 100 billion parameters, these two LLMs can still deliver highly accurate results.
They have been trained with 22 high-quality datasets from diverse sources, making them suitable for use in multiple domains and various use cases. Unlike GPT-3, GPT-NeoX and GPT-J haven't been trained with RLHF. The good news is that both LLMs are available for free through the NLP Cloud API.
4. Vicuna 13-B
Vicuna-13B is an open-source conversational model based on the LLaMa 13 B model. It has been fine-tuned using user-shared conversations gathered from ShareGPT. As an intelligent chatbot, it has countless applications in various industries, such as customer service, healthcare, education, finance, and travel/hospitality.
A preliminary evaluation using GPT-4 as a judge showed that Vicuna-13B achieved more than 90% of ChatGPT and Google Bard quality. It outperformed other models like LLaMa and Alpaca in more than 90% of cases.
5. LLaMA 2
Many leading players in the Large Language Model (LLM) industry have chosen to develop their models privately. However, Meta is breaking this trend by making its LLM available to the public. Meta recently released its open-source LLaMA (Large Language Model Meta AI) and its improved version, LLaMA 2, which is a significant move in the market.
LLaMA 2 is a pre-trained generative text model with 7 to 70 billion parameters designed for research and commercial use. It has been fine-tuned using Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). It is a versatile text model that can be used as a chatbot and adapted for various natural language generation tasks, such as programming. Meta has already launched two versions of LLaMA 2: Llama Chat and Code Llama, which are customizable and open to the public.
6. BLOOM
Launched in 2022, BLOOM is an autoregressive Language Model trained by researchers from Hugging Face and volunteers from over 70 countries. It is designed to generate coherent and accurate text from a prompt by utilizing vast amounts of text data and industrial-scale computational resources.
The release of BLOOM was a significant milestone in making generative AI more accessible. With 176 billion parameters, BLOOM is one of the most powerful open-source Language Models available, capable of providing text in 46 human languages and 13 programming languages. Transparency is a key feature of BLOOM - anyone can access the source code and training data to run, study and improve it.
BLOOM is available for free through the Hugging Face ecosystem.
7. BERT
LLM, or Language Model, is a type of neural architecture that uses a transformer. In 2017, Google researchers developed the transformer architecture in a paper called "Attention is All You Need". One of the first models to use transformers was BERT.

Google released BERT as an open-source LLM in 2018, and it quickly became one of the best-performing models for many natural language processing tasks. Because of its innovative features and open-source nature, BERT is now one of the most widely used LLMs. In 2020, Google announced that it had integrated BERT into Google Search in over 70 languages.
Today, thousands of pre-trained BERT models are available for various use cases, such as sentiment analysis, clinical note analysis, and toxic comment detection. These models are open-source and free to use.
8. Falcon 180B
The Falcon 40B has already impressed the open-source LLM community and ranked #1 on Hugging Face’s leaderboard for open-source large language models. Now, the new Falcon 180B suggests that the gap between proprietary and open-source LLMs is rapidly closing.
The Technology Innovation Institute of the United Arab Emirates released Falcon 180B in September 2023. It is trained on 180 billion parameters and 3.5 trillion tokens, making it an incredibly powerful tool. Falcon 180B has already outperformed LLaMA 2 and GPT-3.5 in various NLP tasks, and Hugging Face suggests that it can rival Google’s PaLM 2, the LLM that powers Google Bard.
It's worth noting that while Falcon 180B is free for commercial and research use, it requires significant computing resources to function properly.
9. Baichuan-13B
China’s pioneering search engine company, Baichuan Inc., has unveiled an open-source large language model named Baichuan-13B, aiming to compete with OpenAI. With a model size of 13 billion parameters, it seeks to empower businesses and researchers with advanced English and Chinese AI language processing and generation capabilities.
The model’s pre-training dataset involves 1.3 trillion tokens. Baichuan-13B enables text generation, summarization, translation, and more tasks. This initiative comes after Baichuan’s success with Baichuan-7B and aligns with the company’s mission to democratize generative AI for broader practical use.
10. CodeGen
The innovative CodeGen model, developed by the Salesforce AI Research team, is an exceptional creation that takes the GPT-3.5 architecture to the next level. With its impressive range of sizes, including 350 million, 2 billion, 6 billion, and a colossal 16 billion parameters, CodeGen is poised to revolutionize the software development industry.
The CodeGen training dataset is an extensive collection of code snippets from multiple programming languages and frameworks, including GitHub and Stack Overflow. With this vast dataset, CodeGen can understand programming concepts and their natural language relationships, allowing it to generate accurate and reliable code solutions from simple English prompts.
Unsurprisingly, CodeGen is garnering attention in the developer community for its potential to streamline software development processes and boost productivity. With CodeGen, developers can save time and focus on more complex tasks, confident that they have a reliable code generator.
11. T5
T5 is a pre-trained language model created by Google AI researchers. It uses the Transformer architecture to handle various natural language processing tasks through a unified "text-to-text" framework. T5 models come in 11 sizes, ranging from small to extra-large, and the largest one has 11 billion parameters.
The model was trained on the Colossal Clean Crawled Corpus (C4) dataset, which includes English, German, French, and Romanian languages. T5 redefines tasks by transforming them into a text-to-text format. This approach facilitates tasks such as translation, summarization, classification, and more by treating each task as a text-generation problem.T5, or Text-To-Text Transfer Transformer, is a versatile pre-trained language model developed by researchers at Google AI. It’s based on the Transformer architecture and designed to handle a wide range of natural language processing tasks through a unified “text-to-text” framework. With 11 different sizes, T5’s models vary from small to extra-large, with the largest having 11 billion parameters.
The model’s training was conducted on the Colossal Clean Crawled Corpus (C4) dataset, encompassing English, German, French, and Romanian languages. T5 redefines tasks by casting them into a text-to-text format, facilitating results like translation, summarization, classification, and more by treating each task as a text-generation problem.
12. MPT-30B
MosaicML is a leading AI research organization that has developed MPT-30B, an innovative open-source language model. With 30 billion parameters, MPT-30B is built on GPT architecture, which has been refined to provide better performance.
MPT-30B has been trained using a unique approach that involves a "mosaic" of data, including 1 trillion tokens of English text and code. This approach combines supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning to provide a comprehensive learning experience.
MPT-30B has commercial applications that include content creation, code generation, and more. MosaicML is committed to open-source innovation, which empowers developers and enterprises to leverage MPT-30B's capabilities for diverse linguistic tasks.
13. Dolly 2.0
Dolly 2.0 is a new AI-powered language generation tool developed by LLM as an alternative to commercial offerings such as ChatGPT. Databricks, a well-known player in the field of AI, created Dolly 2.0, which represents a significant leap in language generation technology. Dolly 2.0 has a 12 billion parameter count and was trained on a dataset called databricks-dolly-15k, which contains 15,000 human-generated prompt and response pairs.
Dolly 2.0 is built on a GPT-3.5 architecture and has been trained on various datasets, which enables it to understand and generate high-quality text. It uses a two-step training process: first, it undergoes pre-training on extensive text corpora, and then it engages in fine-tuning through a pioneering "instruction tuning" approach. Dolly 2.0's release marks a new era for open-source LLM, providing a commercially viable alternative to proprietary models.
14. Platypus 2
Platypus 2 is a powerful player among large language models (LLMs), designed by Cole Hunter and Ariel Lee. With a model size of 70 billion parameters, Platypus 2 has taken the lead on Hugging Face's Open LLM leaderboard. The developers meticulously trained Platypus 2 on the Open-Platypus dataset, consisting of tens of thousands of finely tuned and merged LLMs.
Platypus 2 is built upon LLaMA and LLaMa 2 transformer architectures, combining the efficiency of Qlora and LLaMA 2. Its ability to generate coherent and contextually rich content across various domains sets it apart. Its substantial parameter size and ability to generate high-quality text show its pivotal role in the future of AI-driven applications, from natural language understanding to high-quality content creation.
15. Stable Beluga 2
Stable Beluga 2 is an auto-regressive LLM derived from the LLamA-2 model developed by Meta AI. It is a language model created by Stability AI that can efficiently handle complex language tasks with a high level of accuracy and understanding.
Stable Beluga 2 has been trained on a diverse and internal Orca-style dataset. The model leverages Supervised Fine Tuning (SFT) to improve its performance. This process involves exposing the model to a large corpus of carefully curated examples and guiding it toward better predictions. As a result, it increases its precision and versatility. Additionally, this process enables the model to comprehend context, generate coherent text, and provide valuable insights across numerous apps, including text generation, summarization, and more.
Choosing the Right Open-Source LLM for Your Needs
The realm of open-source LLM (Learning Management Systems) is rapidly expanding. There are currently more open-source LLMs than proprietary ones, and the performance gap between them may be bridged soon as developers worldwide collaborate to upgrade the current LLMs and design more optimized ones.
In this vibrant and exciting context, choosing the right open-source LLM for your purposes may be daunting. To help you out, here is a list of factors you should consider before opting for a specific open-source LLM:
What is your goal for using the LLM? While open-source LLMs are widely available, some may only be suitable for research.
Is an LLM necessary for your project? If not, it might be better to avoid using one to save time and resources.
How important is accuracy for your project? Generally, larger LLMs tend to be more accurate, so consider this when deciding.
How much are you willing to spend on the LLM? Larger models require more resources to train and run, which can add up quickly.
Can a preexisting, pre-trained LLM meet your needs? Many open-source LLMs have already been trained for specific tasks, so it might make sense to use one of those instead of building and training your own from scratch.
Conclusion
Open-source LLMs (language model frameworks) are becoming increasingly popular, which is an exciting development. These powerful tools are evolving rapidly, and it seems like the generative AI space won't be monopolized by only the big players who can afford it.
Currently, there are 15 open-source LLMs available, but the number is much higher and growing quickly.