Speech recognition technology, which is also called Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) or computer speech recognition, enables users to convert audio content into written text. The conversion process involves acoustic and language modeling techniques. It is important to note that speech recognition technology should not be confused with voice recognition, as the former translates audio to text, while the latter is used to identify an individual user's voice.
This technology is widely used across various industries, including transcription services, voice assistants, accessibility features, and more.
What are the key factors that one should consider while selecting a speech-to-text API?
Determining the best speech-to-text API is critical for the success of your project. While speed, accuracy, and affordability are all important factors, the priority order of these attributes should be based on your specific use case and the needs of your end users. To select the ideal transcription service, evaluating and considering various aspects is essential.
Precision: The API should generate highly precise transcriptions, accommodating various speaking scenarios such as background noise, accents, and dialects. High precision is crucial for delivering quality outcomes and enhancing user satisfaction.
Speed: Fast response times and rapid processing speed are necessary for meeting numerous application requirements. Users benefit from low latency, which contributes significantly to the overall functionality and usability of the app.
Cost-effectiveness: An efficient speech-to-text solution must have a reasonable price-to-performance ratio, allowing businesses to maximize return on investment. Inefficiently priced services may hinder adoption and limit integration possibilities.
Modalities: Support for both batch and real-time streaming audio inputs is vital to cater to diverse use case demands.
Functionality: Comprehensive features beyond mere transcription add significant value to downstream processes like improved readability and task utilization.
Scalability: To address fluctuating workloads, a suitable speech-to-text system should effectively manage varying data volumes, serving both startup and enterprise clients efficiently without compromising reliability.
Customizability: Offering tailored models for industry-specific terminology and providing adaptable deployment choices addressing unique privacy, security, and regulatory concerns ensures optimal alignment with client expectations.
Ease of Integration: Simple implementation and seamless platform compatibility contribute to successful adoption. Usage-based billing and ample testing resources facilitate easier evaluation and decision-making during the subscription phase.
Technical Assistance: Competent technical support teams specializing in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing enable prompt issue resolution and ongoing enhancements to ensure long-term success.
What are the most important features of a speech-to-text API?
In this section, we will examine some of the most common features offered by STT APIs. Each API offers different key features, and your use cases will determine which features to prioritize and focus on.
Multilingual support: For organizations working with several languages or dialects, selecting a versatile API capable of managing linguistic diversity is advisable—even for those currently focusing solely on single-language projects. Anticipating potential expansion requires proactive consideration.
Enhanced formatting: Advanced formatting tools encompassing punctuations, number styling, paragraph segmentation, speaker identification, word-level timestamping, profane phrase censorship, and other refinements elevate readability and utility, especially within data analytics contexts.
Auto punctuation and uppercase letters: Although optional depending on intended uses, polished transcript outputs complete with appropriate punctuation and capitalization can eliminate manual reformatting efforts—particularly beneficial for public dissemination purposes.
Profanity filtering: In instances requiring community moderation, APIs incorporating automated obscene term recognition and masking or highlighting mechanisms alleviate burdensome manual monitoring and intervention.
Context comprehension: Leveraging speech-to-text technology primarily aims at gleaning insights from verbal exchanges; therefore, utilizing APIs featuring nuanced language interpretation techniques—such as topic discernment, objective extraction, affect assessment, and condensed synopses generation—enhances user engagement, optimizes categorization, streamlines management procedures, and facilitates informed decisions based on qualitative evaluations.
Specialized lexicon adaptation: When operating in domains characterized by extensive proprietary nomenclature, rare designations, idiosyncratic contractions, or arcane expressions, deploying APIs compatible with customized glossaries ensures superior predictive modeling performance compared to generic alternatives.
Tailored modeling: Beyond keyword enhancement, vendor-offered bespoke training opportunities—utilizing exclusive datasets to calibrate algorithms according to individual demand—provide heightened accuracy and relevance, surpassing conventional stock implementations.
Audio file flexibility: Addressing disparities among incoming audio formats necessitates selecting comprehensive APIs capable of direct processing, circumventing laborious transformative steps, and reducing associated costs.
Common use cases for speech-to-text technology
As noted at the outset, voice technology built on the back of STT APIs is critical to the future of business. So, what are some of the most common use cases for speech-to-text APIs? Let's examine them.
Intelligent personal assistants: Widely known virtual companions such as Siri and Alexa rely upon STT conversion to translate vocal instructions into written actions, fostering smooth communication channels.
Interactive conversational AI: Designed to answer human queries instantly, voicebot systems swiftly convert spoken phrases into text, forming the basis for fluid AI-human dialogues.
Empowering sales and assistance: Equipping sales representatives and customer support professionals with intelligent digital partners help decipher, analyze, and retrieve pertinent information in real time via STT integration, further augmenting professional skills and gauging sales conversations.
Call center operations optimization: Implementing STT technologies in contact centers enables automatic recording, generating transcripts, scrutinizing agent performances, identifying common customer requests, and gathering valuable organizational insights otherwise difficult to obtain.
General speech analysis: Applying STT methods extends beyond call centers, reaching broader domains involving extracted knowledge discovery from auditory data—including boardroom discussions, seminars, conferences, and political addresses.
Accessibility advancements: Utilizing STT technology widens inclusivity horizons, particularly benefiting disabled individuals, deaf populations, classroom students, and attendees at events where instantaneous transcription proves advantageous.
Top Open Source (Free) AI Speech Recognition Models Available on the Market
Choosing an open-source model is recommended for users looking for a cost-effective engine. Here is a list of the best open-source models for automatic speech recognition:
1. DeepSpeech
DeepSpeech is an open-source speech-to-text engine that works in real-time on various devices. The engine operates on GPUs and Raspberry Pi 4 and uses an end-to-end model architecture pioneered by Baidu.
2. Kaldi

Kaldi is a software package for speech recognition that has been highly regarded by researchers for many years. Similar to DeepSpeech, it has good initial accuracy and can facilitate model training. Kaldi has a long testing history and is currently used by numerous companies in their production environments, which boosts developer confidence in its effectiveness.
3. Wav2Letter
Facebook AI Research has developed Wav2Letter, an ASR toolkit that utilizes C++ and the ArrayFire tensor library. It is a moderately accurate open-source library that is user-friendly for smaller projects.
4. SpeechBrain

SpeechBrain is a transcription toolkit that is built on PyTorch. The platform offers open-source implementations of various popular research projects and tightly integrates with HuggingFace, making it easy to access. Overall, the platform is well-defined and regularly updated, which makes it a straightforward tool for training and fine-tuning.
5. Coqui
Coqui is an exceptional toolkit designed for deep learning in Speech-to-Text transcription. It has been developed to cater to over twenty language projects, with various inference and productionization features. Additionally, the platform offers custom-trained models and has bindings for several programming languages, which simplifies the deployment process.
6. Whisper
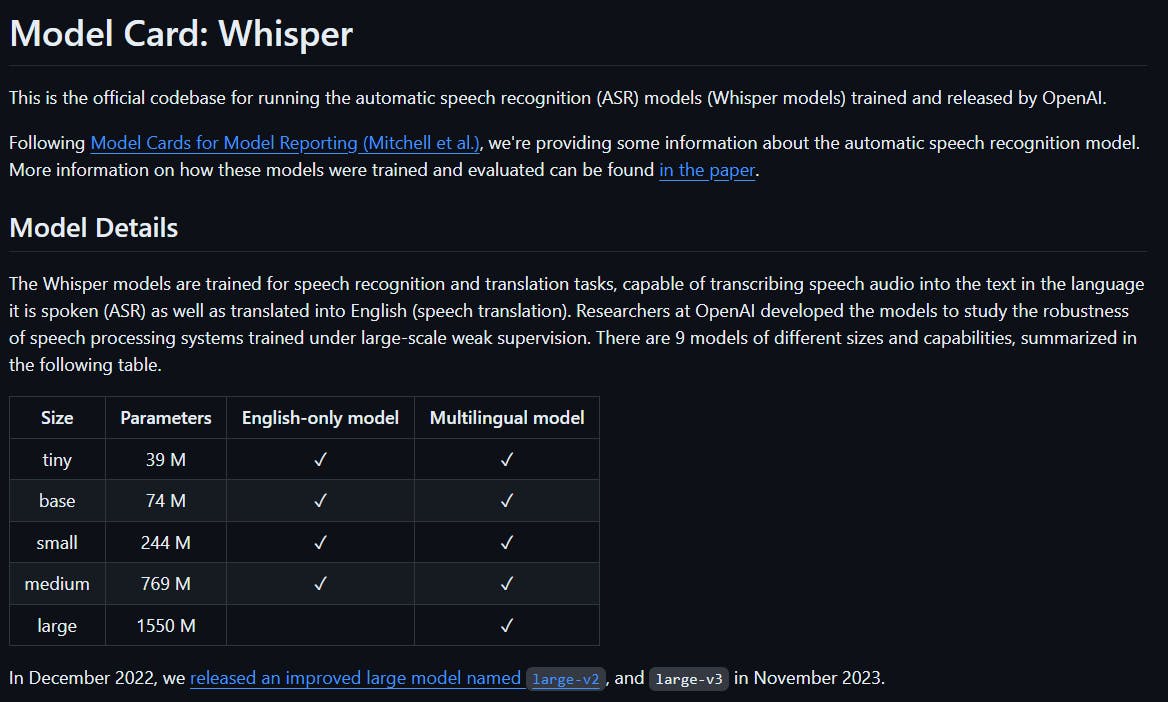
In September 2022, OpenAI released Whisper - a prominent open source option for language translation. This tool offers multiple models with various sizes and capabilities, enabling users to select the most suitable one for their specific requirements. Moreover, Whisper can be utilized either in Python or from the command line and supports multilingual translation.
7. Julius

Julius is a speech recognition software package that was developed at the University of Kyoto in 1991. Despite its age, it still offers a wide range of features, including real-time speech-to-text processing, low memory consumption (less than 64MB for 20,000 words), and the ability to generate N-best/Word-graph outputs. Additionally, it can function as a server unit and has several advanced features.
8. OpenSeq2Seq

NVIDIA has developed an engine for training sequence-to-sequence models, and it has numerous applications beyond speech recognition. This engine is a reliable choice for this particular use case. Users can create their own training models or use preexisting ones. The engine supports parallel processing with the use of multiple GPUs or CPUs.
9. Athena
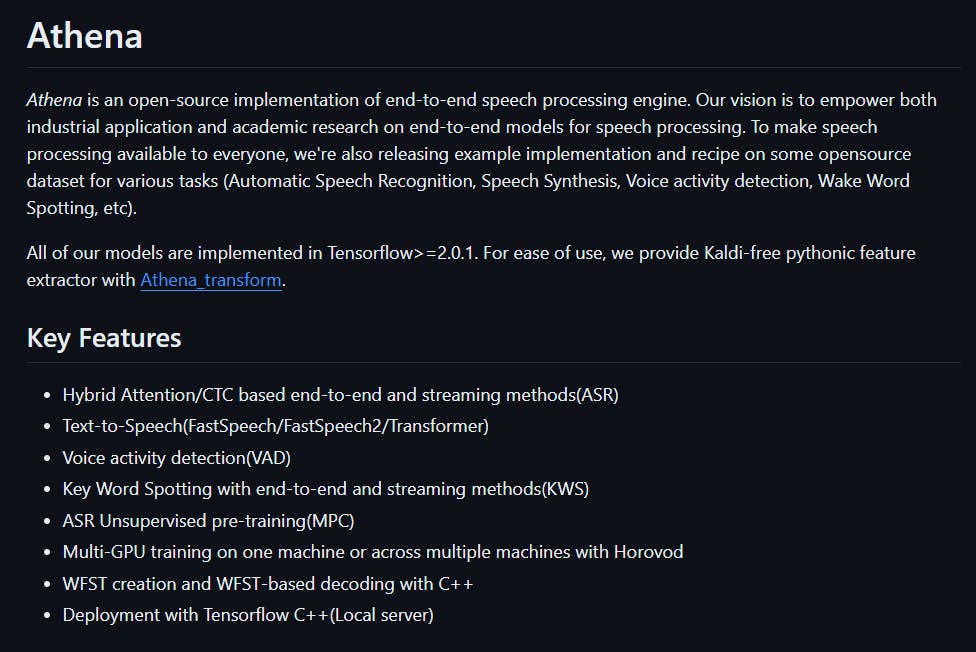
An end-to-end speech recognition engine that uses Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) is written in Python and licensed under the Apache 2.0 license. The engine supports unsupervised pre-training and multi-GPU training on the same or multiple machines. It is built on top of TensorFlow and has a large model available for both English and Chinese languages.
Conclusion
Here are the top 10 speech-to-text APIs in 2024. We hope that this list helps you understand and choose from the many options available in this field. It will also give you a better idea of which provider would be best suited for your specific use case.

