Table of contents
This article will focus on the significant contribution of Web3 technology to AI's success in today's landscape. We'll emphasize three core areas: data, computation, and algorithms. We'll delve into the pressing challenges that AI faces today and explore how Web3 technologies can provide solutions to these challenges.
We'll also present some compelling case studies that highlight innovative AI projects leveraging the existing capabilities of Web3.
The Evolution of Artificial Intelligence
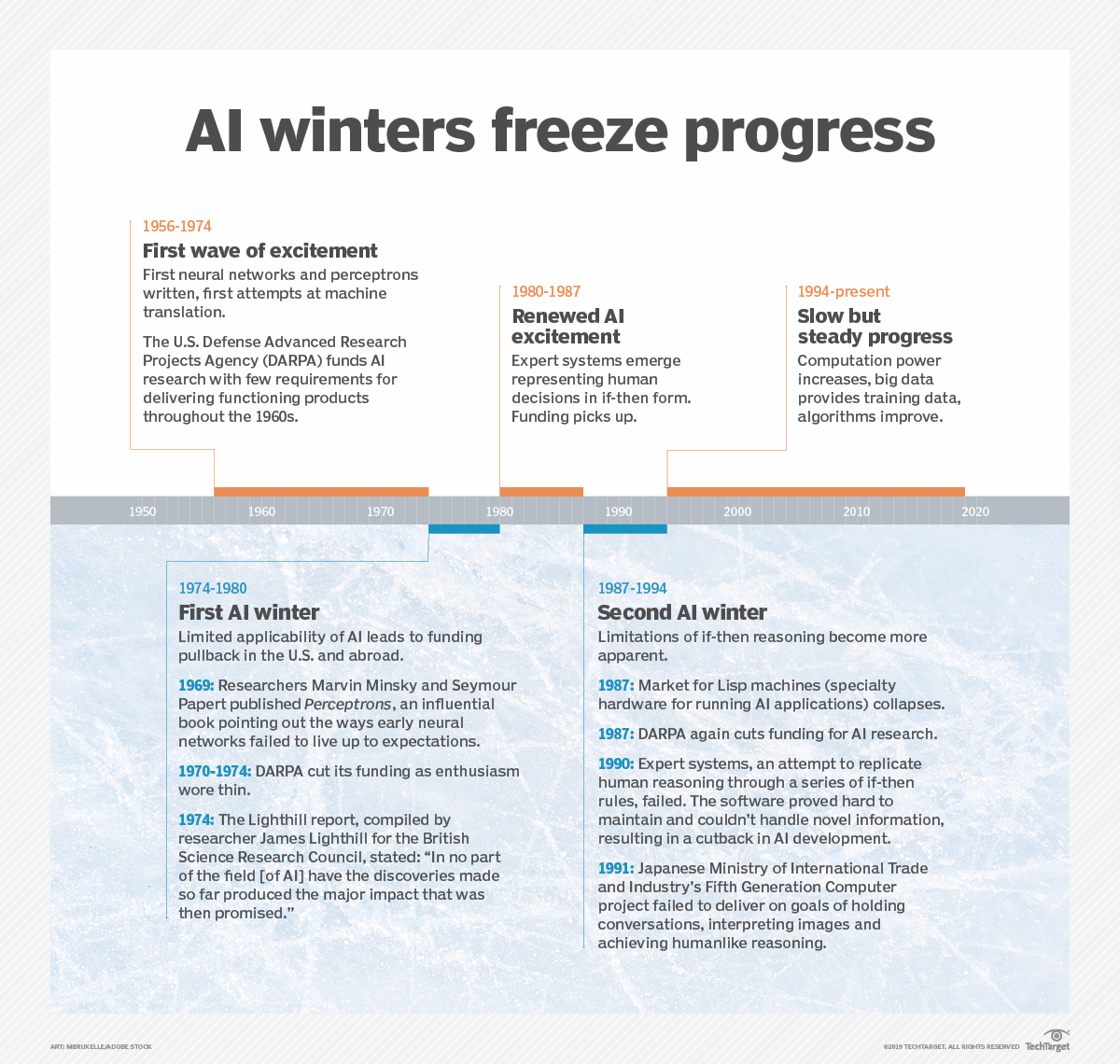
Artificial intelligence (AI) has been around for a while, and it's had three big periods of improvement because of improvements in computers and the Internet.
First AI Expansion (1950s): In 1956, there was a conference about AI called the Dartmouth Conference. People got excited about AI, and early AI programs like the Logic Theorist seemed promising. But because computers weren't very powerful yet, people got disappointed when AI didn't do as much as they hoped. This disappointment led to a time when people weren't as interested in AI, called "the first AI winter."
Second AI Expansion (the 1980s): During this time, people started using expert systems, which are programs that make decisions to solve problems. People also worked on neural networks, which try to imitate how our brains work. However, these technologies had limitations, and there was a time when people lost interest in AI again, called the "second AI winter."
Third AI Expansion (Present): AI is becoming popular again. This time, we have better techniques like deep learning and machine learning, stronger computers, and lots of data to work with. Deep learning methods like CNNs and RNNs have helped AI become good at things like recognizing images, understanding language, and translating languages.
What We Can Learn From AI's History So Far
Three key factors have influenced AI's progress: computing power, data availability, and the Internet.
Computing Power - Increased computing power has allowed AI to solve more complex problems like self-driving cars and medical diagnosis.
Data Availability - The vast amount of data available has helped train and improve AI systems.
Internet - The internet has made collaboration easier for researchers worldwide, speeding up innovation.
These factors have worked together to lay the groundwork for AI's progress, and as technology continues to advance, we can expect even more exciting developments in the future.
More details at: https://ourworldindata.org/artificial-intelligence
The Formula for AI
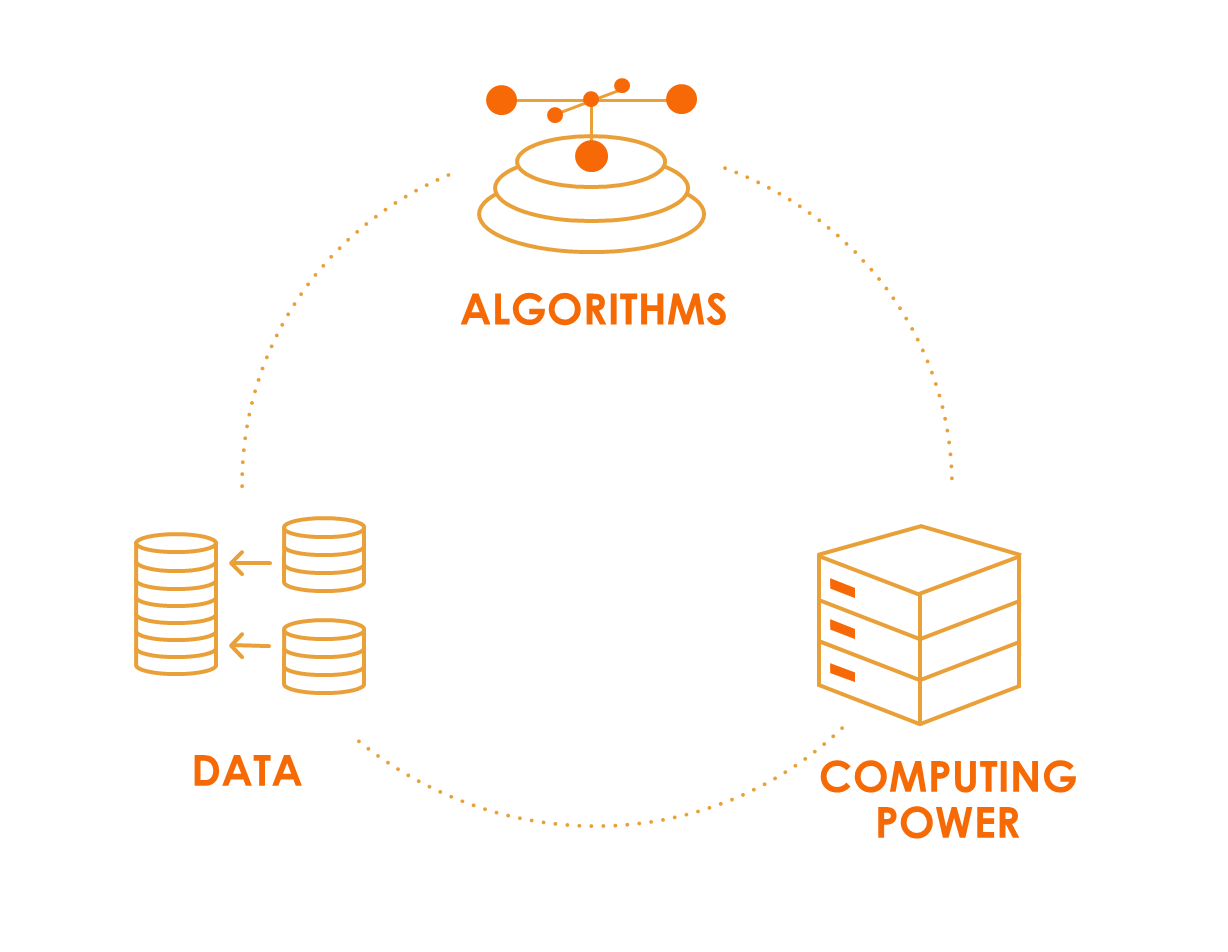
According to the current understanding, the formula for AI is:
Computation + Data + Algorithm = AI
This means that AI needs three things to work properly:
Computation - Hardware like computers and specialized chips do complicated calculations for tasks like image recognition and natural language processing.
Data - AI learns from large amounts of data, identifying patterns and making predictions. Access to a lot of good data helps AI systems better handle real-world situations.
Algorithm - Instructions or rules that tell AI how to process data. Good algorithms help AI learn from data, make correct guesses, and adjust to new situations.
All three parts must work well together for AI to reach its full potential.
Web3 and Data
Data is essential for AI's success. High-quality data is crucial for the development of powerful and reliable AI systems.
Characteristics of Data Required for AI to Succeed
The type of data needed for AI to succeed depends on what it's being used for, but some important qualities include:
Data storage - It is an essential aspect of AI. To ensure that AI algorithms can easily process and analyze data, it should be structured in an easy-to-understand format. Structured data enables efficient model training and data analysis. Additionally, the amount of data available plays a significant role in the performance of AI models. The more data there is, the better the models will generate accurate results.
Data quality - It is crucial for the reliability and trustworthiness of AI algorithms. To achieve this, data must meet three key criteria: accuracy, completeness, and consistency. Accuracy refers to the absence of errors and inconsistencies in the data. Completeness means that data must contain all the necessary information for AI algorithms to make informed decisions. Consistency requires data to be consistent across different sources and periods to ensure its trustworthiness.".
Data readiness - It is essential to consider when developing an AI system. To ensure that the AI system works effectively in real-world situations, the data used must represent the conditions the AI system will encounter during deployment. Additionally, the data must be relevant to the task or problem that the AI system is designed to address. In supervised learning tasks, it is crucial to properly label the data to provide the necessary information for AI algorithms to learn from.
Data Availability - Collecting high-quality data can be time-consuming and expensive. Storing large amounts of data also requires significant storage capacity and infrastructure. Since AI often deals with sensitive personal information, data privacy is of the utmost importance. However, sharing data between entities can be challenging due to privacy and legal concerns.
To ensure the accuracy of AI systems, it is crucial to have data that is available, of high quality, and ready to use. Organizations should address data acquisition, storage, privacy, and sharing challenges to empower AI. By doing so, AI can provide valuable insights, make informed decisions, and effectively solve real-world problems.
How Web3 Can Improve Data Access and Quality for AI Development
In AI, big tech companies hold lots of top-notch data that is perfect for training AI models. However, this data isn't usually available to everyone because these companies keep it to themselves. This means they're the ones in charge of AI innovation.
However, big tech is not the only one making strides in AI. Plenty of researchers and developers in universities, governments, and startups are also doing great work. They face trouble getting their hands on good-quality data that's easy to access and doesn't cost a fortune to store.
In other words, the big challenge is obtaining just the right data—it needs to be top-quality, the right amount, easy to obtain, and not too expensive to keep. That's where Web3 could help.
Collecting high-quality data can be complex and resource-intensive, requiring significant time, money, and specialized knowledge.
Ensuring the privacy and security of sensitive personal information is essential when collecting and using data, and organizations must comply with rigorous regulations to avoid unauthorized access or misuse.
Data integrity is critical for effectively training AI models, but it can be difficult and costly for individuals or small businesses to obtain data that meets the necessary standards of accuracy, completeness, and consistency.
There are solutions available in the form of Web3 that can assist in resolving or easing the difficulties experienced by AI researchers. The principle of decentralization at the core of Web3 has the potential to tackle multiple challenges associated with obtaining valuable datasets for AI development.
1. Decentralized Data Storage
Decentralization of data storage offers significant benefits for AI in terms of cost reduction and security.
2. Cutting Costs
Instead of storing all data in one expensive place, decentralized storage spreads it across many cheaper places. This can save money for AI companies, which usually pay a lot to store data on big servers from big tech companies.
For example, Spheron Network is a project that lets companies store data on a network of many computers instead of one big server and provides computing power to process this data. This makes it cheaper for AI companies to store data, saving them money.
3. Boosting Security
Centralized storage has a big problem: all the data is lost if the main server fails. This could happen because of power cuts, broken equipment, or hackers. Decentralized storage fixes this by storing data on many computers worldwide. If some computers fail, the others keep working, so the data stays safe.
4. Data Ownership, Quality, and Integrity
Right now, big companies usually own the data used to teach AI. This can be a problem because the people who create the data don't get anything. Sometimes, they don't even know their data is being used, which isn't fair.
Also, when AI learns from data collected by others, it might not work very well for everyone. That's because the data might not be accurate or might only represent some groups of people, which isn't fair.
Using blockchain technology, people can own their data and decide who gets to use it. This means they have control over how their data is used and can ensure it's used fairly.
Making Data Clear and Accountable with Web3
On current online platforms (Web2), there's a big problem with not being open about where data comes from and how it's used. This lack of transparency leads to some serious issues:
Data Confusion: When it's unclear where data comes from, it's easy for people to change it and spread wrong information. This can lead to bad decisions based on fake data.
Privacy Problems: Without knowing who's using our data and how our privacy can be invaded. Companies might be tracking us without us knowing, using our data for targeted ads or surveillance.
No One to Blame: If companies aren't clear about how they use data, holding them accountable for any bad practices is hard. This makes it tough to stop unfair treatment or misuse of data.
Hard to Share Data: It's tough to work together and share information without clear data rules. This can slow down progress and block new ideas and products.
Web3 technology, like blockchain, can help solve these issues. It can create a record that shows where data comes from and how it's used, making things more transparent and trustworthy.
Also, new ways of managing data together (decentralized governance) can give people more control over their data, promoting honesty and responsibility in data use.
Empowering Data Owners with Web3
In today's online world, big tech companies usually own and profit from user data, leaving the actual creators with little to no reward.
When people do want to earn money from their data, they often face complicated processes and need to deal with middlemen or complex platforms. This makes it hard for individuals to make money efficiently from their own data. By centralizing data, we limit how it can be used, holding back its full value.
Web3 steps in to change this. It offers a decentralized method that encourages open data access, cooperation, and putting users in control. By giving individuals and groups power over their data and promoting teamwork, Web3 makes it easier to earn money from data, reduce biases, and boost privacy and security.
Web3 on AI Computation
Computational capabilities play a crucial role in the advancement of AI. The effectiveness of AI algorithms and models is often determined by the underlying hardware and software infrastructure that supports them. The computational capabilities of AI systems are typically evaluated based on several key characteristics:
Processing Power: This refers to how fast the CPU, GPU, and specialized AI chips like TPUs and FPGAs can do their jobs. Each one does different things well, so we have to choose wisely based on what we need.
Memory Capacity: AI needs a lot of memory to work with big datasets. Enough memory allows us to process more data simultaneously, making our computations faster.
Bandwidth: AI needs to move lots of data around quickly, especially when learning and doing tasks.
Energy Efficiency: Since AI uses a lot of computing power, we want to use hardware that doesn't waste too much electricity.
Scalability: As AI gets used more, we need to make sure our computers can handle bigger workloads.
In Web2, computation resources are monopolized by centralized companies that invest exorbitant amounts of money into them to hasten AI training and develop more intricate AI algorithms and models. Furthermore, to maintain their competitive edge, they must consistently invest in hardware and overhaul the underlying algorithms to address scaling issues.
To make matters worse, these resources are often underutilized, resulting in inefficient resource allocation and wastage. And let's not forget the colossal energy consumption required to keep the entire system operational.
Centralized computing resources pose a major obstacle for AI startups and researchers because of the exorbitant hardware costs and the significant expenses linked with resources and energy. Fortunately, Web3 has the potential to revolutionize this landscape by providing a more equitable and efficient AI ecosystem through the decentralization of computational resources. With this shift, we can expect an outpouring of innovation and a vast array of AI applications.
The distributed computation blockchain technology has immense potential for AI tasks, particularly for training expansive language models or sophisticated deep learning algorithms. Harnessing a network of distributed resources substantially enhances the processing power available for AI development. This approach proposes an economic framework that rewards participants for contributing computational resources, fostering a self-sustaining ecosystem where AI developers gain access to necessary resources and providers are fairly remunerated in cryptocurrencies or other digital tokens.
This model approach allows AI developers to utilize computational resources as needed without the commitment to substantial infrastructure investments. This model is highly cost-effective compared to traditional cloud services, especially for projects with variable workloads or unpredictable demands.
In summary, the distributed computation blockchain offers a powerful, efficient, and economically viable platform for AI development. Its undeniable benefits make advanced computing resources more accessible to a broader range of innovators.
Web3 for AI Algorithms
Data is the fuel that powers AI, but algorithms are the powerhouse that drives its capabilities. Without algorithms, data remains a collection of meaningless 0s and 1s. Algorithms translate raw data into meaningful insights and intelligent actions, forming the core of "artificial intelligence."
Looking back at the history of AI, we see periodic breakthroughs in algorithm development, each driving a new wave of innovation and advancement. From symbolic AI to machine learning, support vector machines, and deep learning, each generation of algorithms has expanded AI's capabilities and opened up new possibilities.
The complexity and sophistication of AI algorithms have increased significantly over time, making it increasingly challenging for individual researchers or organizations to make significant breakthroughs. This is partly due to the computational demands of modern AI algorithms, which often require specialized hardware and extensive training data.
Fortunately, Web3 technologies offer a suitable framework for facilitating collaborative AI initiatives, emphasizing distributed computing, decentralized governance, and open collaboration. Web3 platforms provide a secure and transparent environment for sharing data, models, and computational resources, enabling researchers and developers to collaborate effectively on AI projects.
Web3’s Incentivization of AI
It is essential to dedicate a separate section to a comprehensive demonstration of the monetization of AI with Web3. We have previously discussed this topic, but it is so crucial that it deserves a more assertive approach. The shift in the profit paradigm that Web3 monetization for AI represents is a game changer, moving from resource controllers' earnings to contributors' earnings.
In Web2, money is usually made like this:
People who gather and move around data make money because they control it.
Those who train artificial intelligence (AI) also make money because they control the data and the methods used to teach the AI.
Companies implementing AI make money by controlling the resources needed to make AI work well and meet market needs.
Now, here are some questions:
Do people who create data make money from it?
Do the people who develop new AI methods make money from their research?
Is everyone involved in improving AI's speed and efficiency, tweaking algorithms, and making small improvements to earn the rewards it deserves?
In reality, the answer is likely to be negative. Although there can be some payment for data collection, patent transfers, licensing, and rewards and salaries for engineers and researchers, it is difficult to ascertain whether contributors receive fair compensation.
Beside the profit made, Other important questions to consider include:
How does the company collect data to make sure the data is accurate?
How can the person who produces and owns the data be sure it's not being used inappropriately without their permission?
How does the AI company prepare the data it receives from suppliers, and how should it be?
How can the person or company using resources in this process be sure they're not paying too much for what they're getting?
The answers to these questions are insufficient within the confines of the Web2 paradigm. To overcome these challenges, it is time to embrace the advancements of Web3 technologies, which greatly emphasize decentralization, tokenization, transparency, and open collaboration. Web3 empowers individuals and organizations to take charge of their data and provides mechanisms for sharing AI models and computational resources, fostering a more inclusive and equitable AI ecosystem.
In Web3:
People who create data get paid for what they contribute.
Those who gather and move data around get paid for doing so.
People who invent algorithms get paid for their valuable creations.
Companies specializing in AI get paid for providing computational power, training, and important data.
Production companies make money by selling what they make, and they can use blockchain technology to reduce misuse of their products.
Arguably, there can be new kinds of markets, such as:
High-quality data is more valuable in data markets because it's treated like an asset.
In data processor markets, different companies specialize in processing different data types. They make money by providing ready-to-use data to customers, like AI trainers, who need it to improve their models.
In AI model markets, there's a place where people can buy and sell different AI models. Users can pick the one that suits their needs best, creating a marketplace that focuses on finding the right AI model for each job.
Application markets are similar to regular app stores, where people buy the apps they want to use. However, in Web3, a feature called on-chain access control helps prevent misuse and makes the environment more secure for app providers and users.
The utilization of Web3 and its incentivizing mechanism ensures that individual players in the AI cycle are rewarded fairly for their efforts or face appropriate consequences for any malicious behavior.
Conclusion
The intersection of AI and Web3 holds tremendous promise for transforming various sectors and industries. By leveraging both technologies' strengths, we can create more effective, transparent, and ethical AI systems that benefit society.
From data management to computation and algorithm development, Web3 technologies like blockchain and decentralized networks can potentially resolve some of the most pressing concerns facing the AI sector. These technologies enable greater collaboration, transparency, and incentivization, ultimately leading to better AI models, improved data quality, and more equitable distribution of resources.
While there are still challenges to overcome, the future looks bright for AI and Web3. As these technologies continue to evolve and mature, we can anticipate groundbreaking innovations and applications that will reshape the way we live, work, and interact with one another. Ultimately, the fusion of AI and Web3 has the potential to bring about a new era of growth, collaboration, and positive transformation. It's up to us to harness this potential and create a brighter future for all