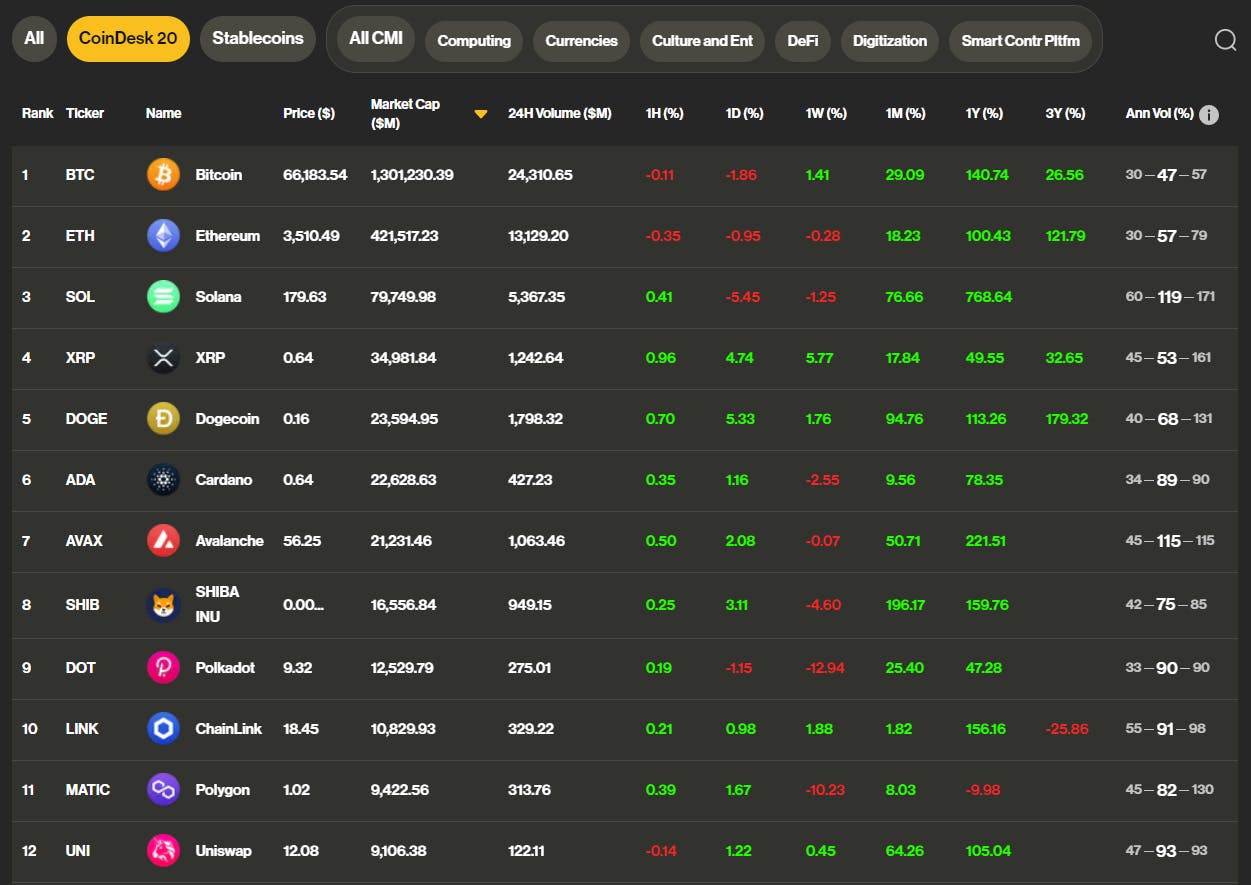
Ethereum's long-awaited "Dencun" upgrade has been activated, marking a significant milestone for the blockchain's growth and development. This technically complex hard fork, which occurred at Ethereum epoch 269,568 at 13:55 UTC (9:55 a.m. ET), is set to reduce data fees and spur growth on layer-2 networks such as Arbitrum and Polygon. Despite the upgrade's potential to disrupt the market, the price of Ethereum's native cryptocurrency, ether (ETH), remained relatively stable. However, it's worth noting that ETH has increased by 50% over the past month, in line with the CoinDesk 20 Index's 49% rise over the same period.
The blockchain community is eagerly awaiting the much-anticipated Ethereum upgrade, which is considered to be the biggest one in almost a year. The upgrade promises to revolutionize the blockchain by introducing a new storage space for data on the blockchain called "blobs," with a dedicated area that is separated from regular transactions, and at a lower cost. This is expected to usher in a new era for tackling Ethereum's notoriously high transaction fees. Moreover, the upgrade has triggered a race among the biggest layer-2 networks to take advantage of the changes in scaling the blockchain.
During the official watch party hosted by EthStaker and the Ethereum Foundation, Terence Tsao, core developer of Offchain Labs, revealed that some larger rollups are holding off on submitting data blobs to Ethereum until the network is more stable. However, the Arbitrum Foundation's X account assured that it would start using blobs. Meanwhile, the layer-2 network Starknet has already confirmed that it has started submitting data blobs.
Blast, a layer-2 network, reported at least one casualty due to issues related to Ethereum's Dencun upgrade. Blast stopped producing blocks but later tweeted that the issue had been resolved. A full analysis of the incident will be shared shortly.
What is proto-danksharding?
The upgrade is centered around the implementation of "proto-danksharding" - an innovative transaction category that stores data on Ethereum through the introduction of data blobs. Although the primary advantage of this upgrade may not be for Ethereum users directly, it will significantly benefit layer 2 networks such as Arbitrum, Optimism, and Polygon, which help scale Ethereum by bundling up transactions from users and passing them back to the main blockchain for settlement in large batches.
Rollup networks have become increasingly popular in the Ethereum ecosystem over the past few years, and users have already deposited billions of dollars in these chains. Recently, these networks have experienced higher transaction volumes compared to the base chain.
With the implementation of Dencun, layer-2s will now be able to post data to Ethereum in a more streamlined and efficient way, avoiding the current clunky transactional data fields. This will significantly reduce settlement time and costs for rollups, which will ultimately benefit end-users by slashing their fees. Dencun is the first step towards Ethereum's goal of implementing "sharding," a technological feature that will divide the blockchain into mini-chains to process more transactions at lower costs. While the full implementation of sharding is still years away, Dencun's proto-danksharding is a promising interim solution to tackle Ethereum's high gas fees. Don't believe me? Check out the screenshot of the blockchain explorer Beaconcha. in, which shows the first Ethereum blocks after the activation of the Dencun upgrade!
Data availability solutions
Proto-danksharding is essential to reap the benefits of a new class of blockchains that have entered the Ethereum ecosystem, known as data availability (DA) layers. Celestia, EigenDA, and Avail are some of the DA layers that help networks store large amounts of data for rollups. It is important to note that DA’s are separate blockchains that prove that the data for these transactions exists and is readily available if needed. As rollups produce a lot of data and consume a lot of data space on Ethereum, the need for DA solutions has become even more crucial. Proto-danksharding, therefore, plays a critical role in reducing the costs of downloading DA data, making it a cost-effective solution.
Layer-2 fee race
With the drop in layer-2 fees among Ethereum's rollups, it seems that a fee war could be on the horizon. These auxiliary networks will be competing fiercely for users by offering cheaper transaction fees. While the full impact of proto-danksharding remains to be seen, it is clear that the competition will be intense. In a recent interview with CoinDesk, Jesse Pollak, creator of Base, the U.S. crypto exchange Coinbase's layer-2 network, stated that unless there is a significant increase in usage, costs could drop by as much as 90% to 95%.
According to Steven Goldfeder, the co-founder of Offchain Labs, the largest Ethereum layer-2 network based on TVL, each ecosystem will ultimately determine how they price transaction fees. Goldfeder also pointed out that some competitors price layer-2 fees at zero, which is not sustainable.
Other layer-2 experts believe that Dencun will encourage collaboration between rollup projects. They argue that scalability is the key to unlocking permissionless collaboration between developers across projects and teams. Karl Floersch, the CEO of OP Labs, the firm behind the Optimism blockchain, explained that with Dencun, developers across the Ethereum ecosystem can seamlessly build together. The upgrade will enable a group of loosely coordinated developers to build systems that provide overall experiences that will rival the user experiences on top-down, centrally planned platforms.
What else is in Dencun?
The Dencun upgrade is primarily centered around proto-dank sharding, but developers should also note the eight other Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) included in the Dencun package, as they will significantly impact their work.
EIP-1153: This helps reduce fees for storing data on-chain, improving block space.
EIP-4788: improves designs for bridges and staking pools.
EIP-5656: a small code change that should improve the Ethereum Virtual Machine.
EIP-6780: eliminates a code that could terminate smart contracts.
EIP-7044: a minor code change that should improve the staking user experience.
EIP-7045: expands the attestation slot inclusion range.
EIP-7514: will slow down the rate of staking on Ethereum.
EIP-7516: helps rollups get information about the cost for blob transactions.